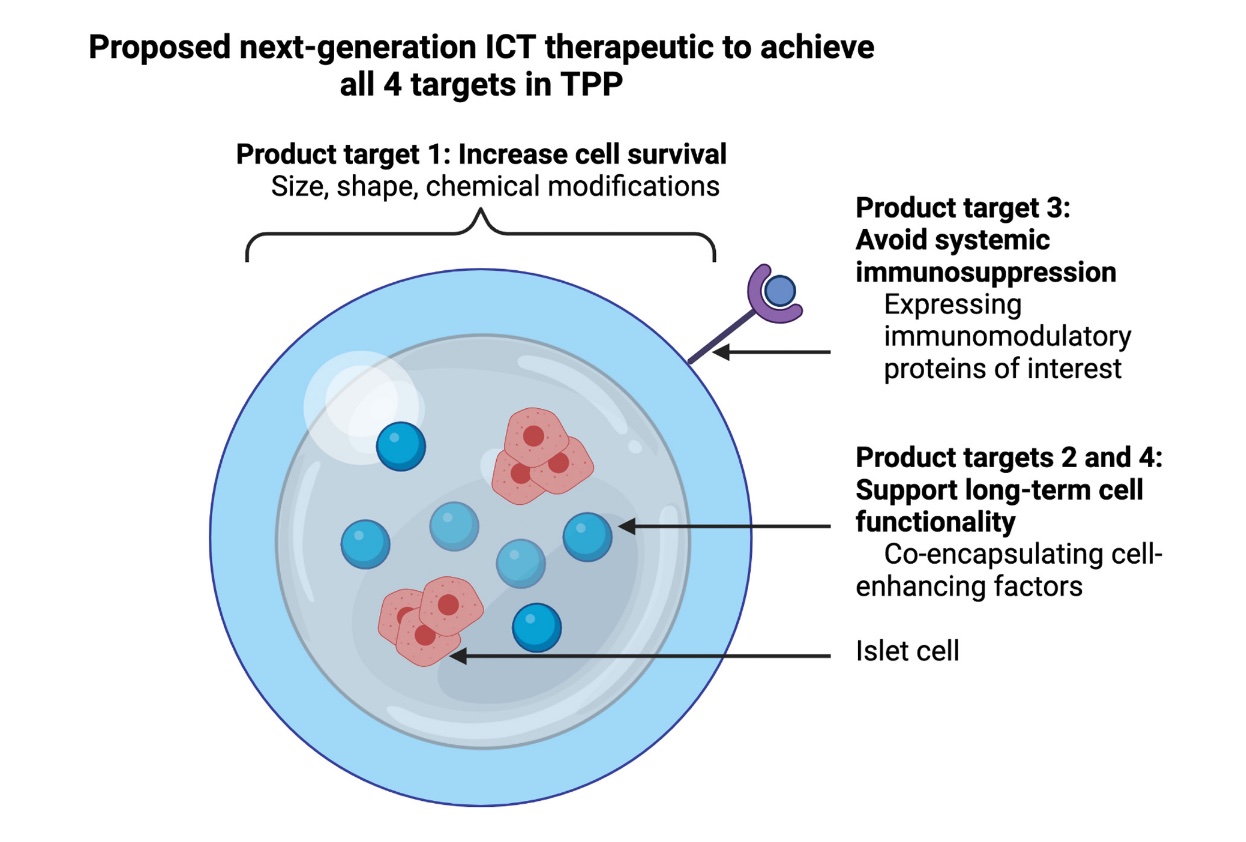
Despite optimal insulin replacement therapy, more than 40% of patients living with type 1 diabetes (T1D) experience severe hypoglycemic reactions and many others experience complications of their disease like vascular and renal damage. These patients require less burdensome and potentially curative approaches for their T1D, most notably including islet cell transplantation (ICT). Previous clinical testing proved the novel therapy successful in initial establishment of insulin independence but low islet viability, functionality, and localized immune protection limits ICT currently as a therapeutic for T1D. In order to address these limitations, Dr. Fatma Dogan and her team at VIC present a review on potential solutions that challenge ICT and promising combinatorial approaches that can optimize this therapeutic approach while clearly targeting the desired clinical outcomes.
Recent FASEB publication from the VIC team presents a review on a potential comprehensive definition of a target product profile for optimizing islet cell transplantation for treating and potentially curing type 1 diabetes